What Makes the Olympus EVIS X1 One of the Most Advanced Endoscopy Systems on the Market
admin
January 30, 2026

Introduction
Digestive endoscopy has reached a new level of sophistication in recent years. Among the most advanced platforms available today, the Olympus EVIS X1 stands out as a system that goes beyond incremental upgrades, combining advanced imaging, intelligent image processing, and strong clinical focus.
In this article, you will understand what makes the EVIS X1 one of the most advanced endoscopy systems on the market, its key technological differentiators, and in which clinical scenarios it delivers the greatest value.
What Is the Olympus EVIS X1?
The EVIS X1 is Olympus’ next-generation digestive endoscopy platform, designed to significantly improve diagnostic accuracy—especially in the early detection of gastrointestinal lesions.
Unlike previous generations, the EVIS X1 was developed with a strong emphasis on:
Superior image quality
Advanced image-enhancement technologies
Intelligent integration of hardware and software
Direct clinical decision support
Rather than being a simple hardware evolution, the EVIS X1 represents a paradigm shift in endoscopic imaging.
Image Quality: A New Standard in Digestive Endoscopy
One of the most noticeable advances of the EVIS X1 is its significant improvement in image quality. The system delivers sharper images, enhanced contrast, and greater detail of mucosal structures.
In clinical practice, this translates into:
Clearer visualization of vascular patterns
Better definition of lesion margins
Reduced loss of detail in challenging anatomical areas
These improvements directly increase physician confidence during examinations.
Advanced Imaging Technologies That Truly Matter
The EVIS X1 integrates well-established Olympus technologies while introducing new imaging tools designed specifically to support early lesion detection.
🔹 Narrow Band Imaging (NBI)
A widely recognized technology that enhances visualization of superficial vascular patterns and mucosal structures, supporting lesion characterization.
🔹 Texture and Color Enhancement Imaging (TXI)
One of the most important innovations of the EVIS X1. TXI enhances:
Mucosal texture
Color contrast
Subtle differences between healthy and abnormal tissue
In routine clinical use, TXI helps identify abnormalities that may be difficult to detect with standard white-light imaging.
🔹 Enhanced White Light Imaging (WLI)
Even in conventional white-light mode, the EVIS X1 provides noticeable improvements in brightness, contrast, and color fidelity.
Intelligent Imaging Supporting Clinical Decision-Making
Beyond image clarity, the EVIS X1 reflects a broader evolution in endoscopy: technology actively supporting the physician.
The system is designed to:
Reduce inter-observer variability
Improve diagnostic consistency
Enhance detection of subtle and early-stage lesions
This is particularly valuable in high-volume screening and routine diagnostic examinations.
Compatibility With Advanced Endoscopes
The EVIS X1 is fully compatible with Olympus’ latest-generation endoscopes, ensuring:
Optimal integration between processor and scope
Full utilization of imaging technologies
Operational stability in high-throughput clinical environments
For clinics and hospitals, this compatibility translates into long-term investment protection.
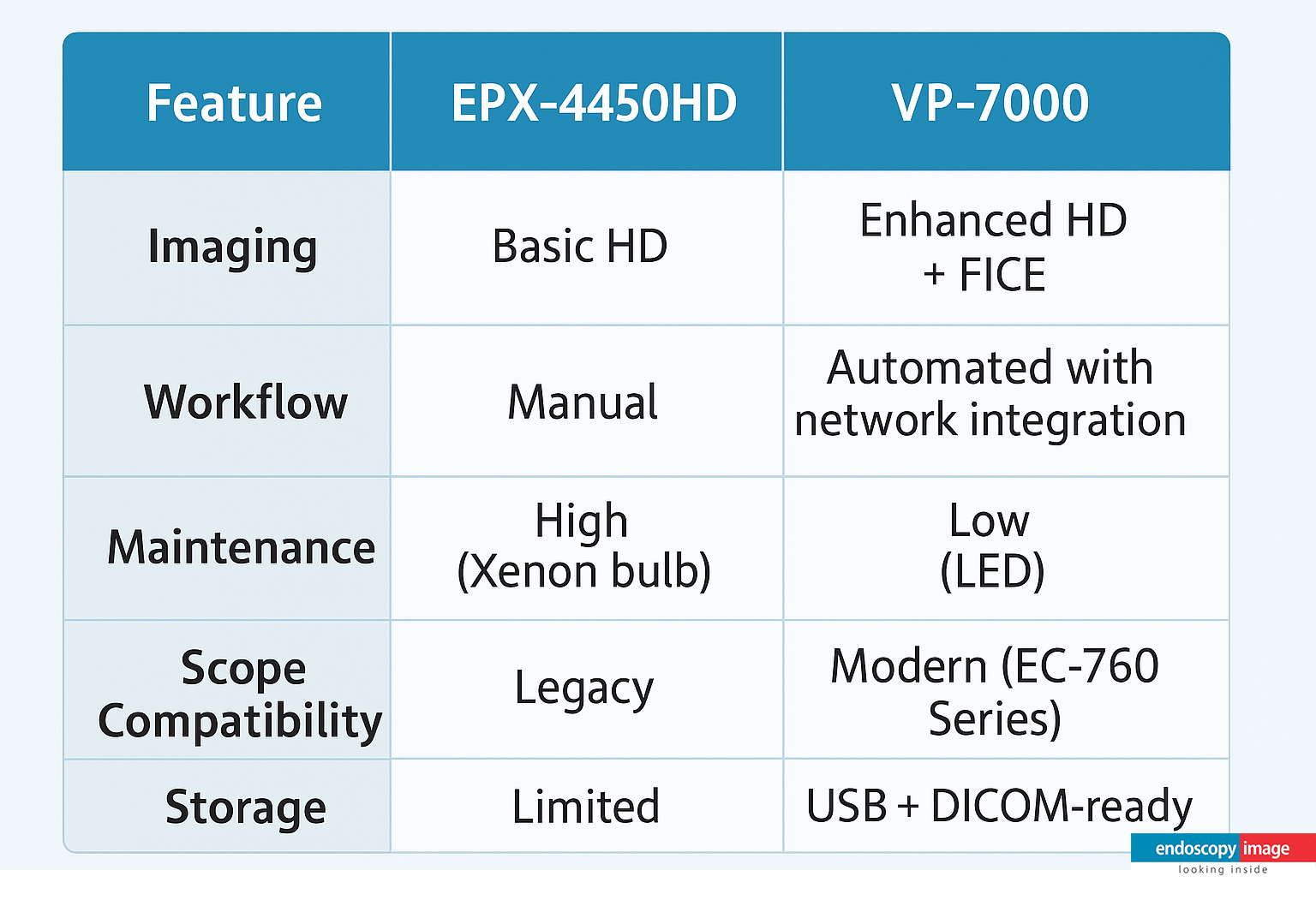
EVIS X1 vs Previous Olympus Platforms: What Has Really Changed?
Compared to earlier systems such as the CV-190, the EVIS X1 introduces clear advancements:
More sophisticated image processing
New enhancement technologies such as TXI
Improved performance in early lesion detection
A platform designed for future innovation
This is not merely an incremental upgrade, but a significant technological leap forward.
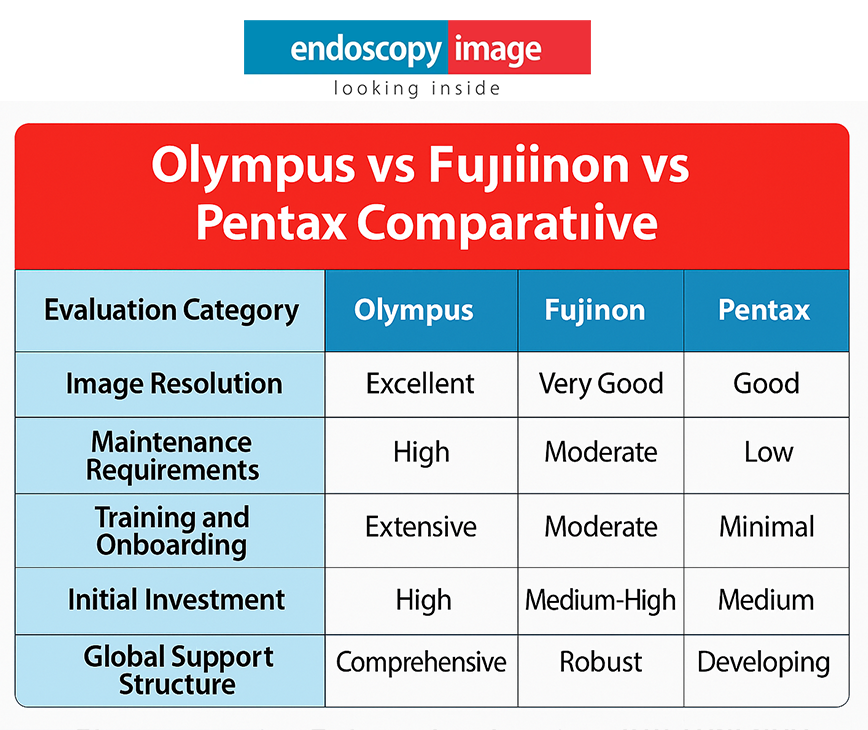
Who Is the Olympus EVIS X1 Best Suited For?
The EVIS X1 is particularly well suited for:
High-volume clinics and hospitals
Centers focused on early cancer detection
Institutions seeking technological differentiation
Organizations planning long-term investments in endoscopy
While positioned as a premium system, its value lies in diagnostic performance, workflow efficiency, and clinical confidence.
Is the Olympus EVIS X1 Worth the Investment?
From a technical and clinical standpoint, the EVIS X1 is among the most advanced endoscopy systems currently available. However, the decision to invest should consider:
Clinical profile and case mix
Examination volume
Available budget
Medium- and long-term strategic goals
In many cases, investing in the EVIS X1 means raising the diagnostic standard of care, improving clinical outcomes, and strengthening institutional reputation.
Conclusion
The Olympus EVIS X1 is not simply a more modern system—it represents a new generation of digestive endoscopy, focused on precision, intelligent imaging, and real clinical impact.
Endoscopy Image supports physicians, clinics, and hospitals in evaluating whether the EVIS X1 is the right solution for their clinical and operational needs, including new and refurbished options, always with a focus on safety and cost-effectiveness.
FAQ: Olympus EVIS X1 One of the Most Advanced Endoscopy Systems
➡️ The Olympus EVIS X1 introduces advanced image processing, including Texture and Color Enhancement Imaging (TXI), improved Narrow Band Imaging (NBI), and enhanced white-light imaging. Compared to earlier platforms like the CV-190, it offers superior image clarity, better lesion visualization, and stronger support for early gastrointestinal lesion detection.
➡️ TXI (Texture and Color Enhancement Imaging) enhances subtle differences in mucosal texture and color contrast. This allows physicians to more easily identify early-stage lesions or abnormalities that may be difficult to detect using standard white-light imaging alone, improving diagnostic confidence and accuracy.
➡️ Yes. The EVIS X1 is designed for high-throughput clinical environments, offering stable performance, compatibility with advanced Olympus endoscopes, and imaging technologies that support consistent diagnostic quality. It is especially suitable for hospitals and clinics focused on screening programs and early cancer detection.
Topics that might interest you:
Blog & Articles
What Makes the Olympus EVIS X1 One of the Most Advanced Endoscopy Systems on the Market
Discover the key differences between endoscopy and colonoscopy procedures. Expert guide for medical..
Complete Guide to Next-Generation Digestive Endoscopy Equipment (2026)
Discover the key differences between endoscopy and colonoscopy procedures. Expert guide for medical..
Endoscopy Equipment in Mexico and Latin America: Your Complete 2025 Buying Guide
Discover the key differences between endoscopy and colonoscopy procedures. Expert guide for medical..
Endoscopy and Colonoscopy: The Complete Guide to Understanding Procedure Differences in 2025
Discover the key differences between endoscopy and colonoscopy procedures. Expert guide for medical..